Smart Pole Market Size to Reach USD 46.92 Billion by 2034
The global smart pole market size is estimated to reach around USD 46.92 billion by 2034 increasing from USD 11.76 billion in 2024, with a CAGR of 14.84%.
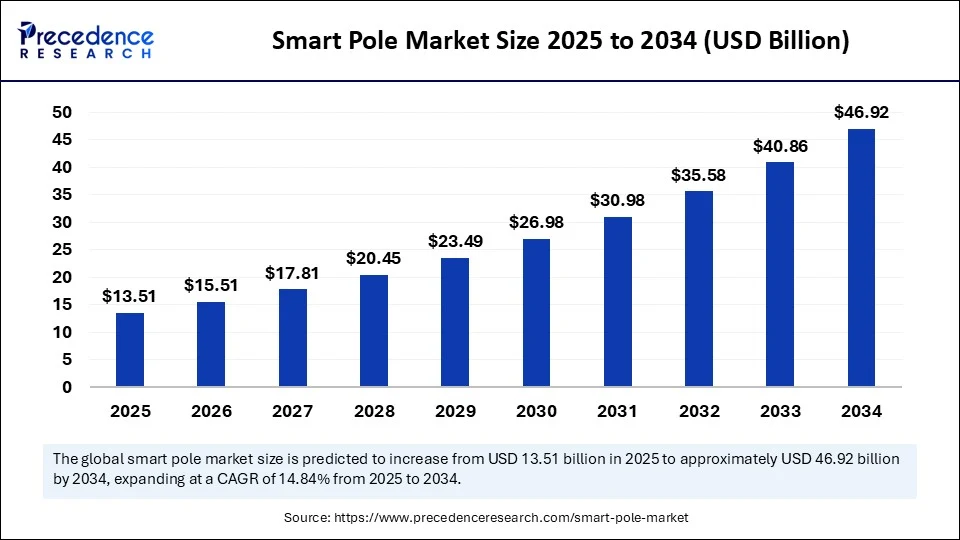
Smart Pole Market Key Takeaways
- In terms of revenue, the global smart pole market was valued at USD 11.76 billion in 2024.
- It is projected to reach USD 46.92 billion by 2034.
- The market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 14.84% from 2025 to 2034.
- North America dominated the largest smart pole market share of 34% in 2024.
- Asia Pacific is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 20.8% during the foreseeable period.
- By offering, the hardware segment accounted for the biggest market share in 2024.
- By offering, the software segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 22% during the foreseeable period.
- By installation type, the retrofit segment contributed for the highest market share in 2024.
- By installation type, the new installation segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the foreseeable period.
- By application, the highways and roadways segment captured the remarkable market share in 2024.
- By application, the public places segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 20% during the foreseeable period.
- By connectivity tech, the cellular (4G/5G/NBIoT) segment accounted for the largest market share in 2024 and expected to sustain its position during the foreseeable period.
- By material, the metallic segment generated the major market share of share in 2024.
- By material, the composite segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 21% during the foreseeable period of 2025-2034.
How is AI Transforming the Smart Pole Market?
AI integration with smart poles represents a leap forward in building intelligent cities. These poles can foresee traffic congestion by analyzing patterns from past and present data, guiding vehicles through less crowded routes. Beyond traffic, smart poles adapt lighting to match real-time pedestrian and vehicle density, conserving energy and reducing environmental impact. Enhanced with AI-powered surveillance, they also contribute to safer urban environments through rapid threat identification and response.
Get Sample@ https://www.precedenceresearch.com/sample/6419
Market Overview
Smart poles are redefining how cities approach street infrastructure—as intelligent, connected nodes rather than isolated lighting fixtures. A smart pole typically combines LED lighting, network connectivity (e.g. cellular small cells, Wi‑Fi), environmental and surveillance sensors, digital signage, and increasingly, edge computing and EV charge points.
This multifunctional evolution is fueled by the convergence of smart lighting initiatives, 5G rollout requirements, and growing demand for urban analytics. Once limited to experimental smart city patches, smart poles now form part of mainstream city planning, with deployments in urban centers, campuses, highways and public transport corridors. The market encompasses manufacturers of hardware (poles, lamps, sensors, power units), software and platform providers (for control systems and analytics), telecom providers, systems integrators, and smart city utilities.
Market Drivers
-
Advances in IoT and sensor mainstreaming: Sensor technologies—air‑quality, noise, temperature, motion detection—are increasingly compact and affordable. Embedding them into poles allows continuous environmental monitoring and situational awareness that cities can leverage for responsive policy, health alerts, or traffic control.
-
Rapid expansion of 5G and need for small‑cell sites: Telecom operators are required to deploy dense small‑cell networks to deliver 5G coverage. Smart poles act as dual‑use infrastructure, supporting city functions while hosting telecom equipment—reducing aesthetic and logistical barriers to densification.
-
Shift toward managed city services: Cities prefer centralized control platforms that unify lighting, signage, sensors and connectivity. Smart pole networks that tie into centralized dashboards or municipal IoT platforms become backbone infrastructure for operational intelligence and policy enforcement.
-
Cost savings via energy‑efficient lighting: LED integration, intelligent brightness control, motion detection, and smart scheduling reduce energy consumption and maintenance cycles. This is especially persuasive for cities with aging lighting systems moving toward sustainability.
-
Public safety and enhanced surveillance: High‑definition cameras, public‑address systems, gunshot detection, face recognition (where permitted), and real‑time analytics elevate public safety capabilities. Broad surveillance coverage bundled with lighting creates value for law enforcement and emergency response systems.
Market Opportunities
-
Edge computing at the pole base: Embedding AI/ML processing modules onsite enables latency‑sensitive analytics (e.g. pedestrian crowd analysis, traffic monitoring, incident detection) without constant backhaul to central data centers. This edge approach reduces bandwidth usage, speeds reaction times and allows data privacy controls.
-
Sensor ecosystem expansion: Cities are broadening use cases for sensors—monitoring air pollution, humidity, noise levels, radiation, temperature, footfall, or even wireless occupancy tracking. Poles can serve as persistent, distributed environmental infrastructure.
-
Digital signage and interactive public services: High‑resolution display panels, touch interfaces and proximity sensors enable dynamic advertising, way‑finding, public information boards, or emergency alerts—turning street columns into public service kiosks.
-
Integrated EV charging: With the global acceleration in electric vehicle adoption, smart poles equipped with chargers (AC or DC fast‑charging sockets) offer access to curbside or sidewalk charging without separate infrastructure. This is especially useful in dense urban areas lacking parking garages.
-
Infrastructure convergence with utilities: Smart poles are beginning to serve not just lighting and connectivity, but also municipal utilities such as metering (water, gas, electricity), traffic signal control, environmental monitoring, telecom backhaul, and emergency systems, thereby consolidating infrastructure into a unified street asset.
Market Challenges
-
Hardware modularity vs. standardization: While modular designs are flexible, absence of open standards means module vendors may remain proprietary. Cities risk vendor lock‑in and compatibility issues when upgrading or expanding systems from different suppliers.
-
Urban aesthetic and planning constraints: Smart poles introduce bulkier, taller structures—and some communities resist changes to historical areas or scenic streetscapes. Obtaining permits, satisfying architectural review boards, and assuring minimal visual impact are non‑trivial.
-
Cybersecurity and data privacy: Embedded surveillance cameras, wireless connectivity, edge compute nodes—if inadequately secured—introduce vulnerabilities. Cities must implement encryption, secure OS architectures, and privacy‑by‑design frameworks especially if collecting visual or personally identifiable data.
-
Financing complexity and budget fragmentation: Capital cost, maintenance expense, telecom fees and implementation overhead span municipal, private and operational budgets. Fragmented financial responsibility can slow or stall smart pole projects.
-
Maintenance logistics: With diverse hardware integrated in one structure, maintenance requires coordination across lighting, telecom, sensors, signage and charging sub‑systems. Cities need robust asset management, reporting, and preventive maintenance regimes.
Recent Developments
-
Next‑generation prototypes unveiled: During 2024 and early 2025, multiple technology vendors have showcased smart pole prototypes featuring onboard GPUs for AI video analytics, replaceable sensor bays, solar‑charged battery packs, wind turbine elements, and adaptive lighting algorithms.
-
POC to full‑scale citywide rollouts: Municipalities that had limited pilot installations are now scaling up to full networks, deploying hundreds to thousands of units in central business districts, transit corridors and public parks. These deployments include operational dashboards integrated with city command centers.
-
Public–private strategic alliances: Smart pole integrators and telecom operators are forming formal strategic partnerships—jointly investing in infrastructure to host small‑cells, Wi‑Fi and digital signage, sharing revenues and lowering risk for both parties.
-
Sustainability and ESG alignment: New smart pole projects are being marketed as carbon‑neutral or carbon‑tracking infrastructure, with solar‑LED hybrids, recyclable structural materials and energy‑consumption monitoring dashboards that align with city sustainability pledges.
-
Data‑driven services expansion: Cities now offer APIs or public data platforms that monetize anonymized data from smart poles—such as pedestrian heat maps or air‑quality metrics—for startups, mobility planners, and retail analytics firms.
-
Standard development progress: Industry groups and smart city alliances are advancing draft standardization guidelines for interoperability across sensor modules, lighting control protocols, telecom mounting, and security frameworks—signaling higher scalability and vendor neutrality in the near future.
Smart Pole Market Companies
- Acuity Brands Lighting
- American Tower Corporation
- Bivocom
- Cree Inc.
- Efftronics Systems
- ELKO EP
- GE (General Electric)
- HUB Group
- iRam Technologies
- Kesslec
- Lumca Inc.
- Mobile Pro Systems
- Norsk Hydro ASA
- Signify Holding
- Shanghai Sansi Electronic Engineering
- Siemens AG
- Sunna Design
- Telensa Limited
- Wipro Lighting
- Zumtobel Group
Segments Covered in the Report
By Offerings
- Hardware (poles, luminaires, sensor modules, communication devices, controllers)
- Software (management, analytics platforms)
- Services (installation, maintenance)
By Installation Type
- New Installation
- Retrofit Installation
By Application
- Highways & Roadways
- Public Places (parks, plazas)
- Railways & Harbors
By Connectivity Technology
- Cellular (4G/5G/NBIoT)
- Wi-Fi, Zigbee, Bluetooth, Fiber, PLC
By Material
- Metallic (steel, aluminum)
- Composite (emerging lightweight materials)
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
Also Read: https://www.precedenceresearch.com/
